Backfilling helps ensure data consistency and completeness by re-syncing source data to destination shares under specific scenarios.
The Backfill process transfers all historical source data to a destination share in a single synchronization and resets the schema on the destination table when loading a data warehouse.
When does a Backfill occur?
Users can manually trigger a backfill in two ways:
Transferring data for the first time to a new share.
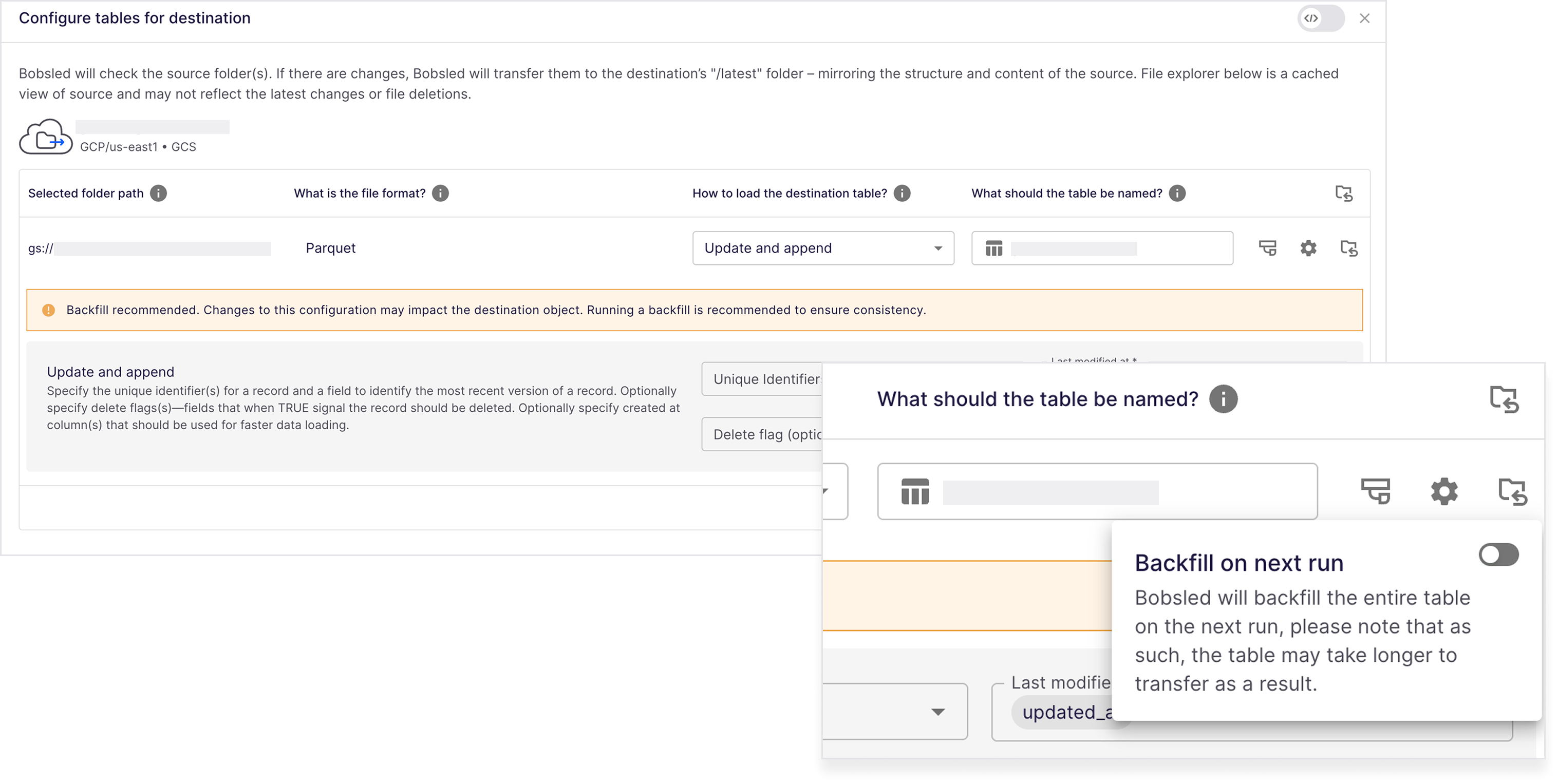
Selecting Backfill on Next Run or Backfill all while editing a transfer in the Bobsled Application.
When is a Backfill recommended?
Bobsled will alert in the application when a backfill is recommended to ensure data consistency, under the following conditions:
Modifications to source or destination locations.
Changes in loading or unloading behaviors, including settings like
primaryKeys,deleteFlags, orfileOptions.Updates to glob filters or source view definitions.
NOTE:
Not enabling backfill when recommended may result in inconsistent data or a failed transfer. If a transfer fails as a result, you can manually trigger a backfill later from the UI.
Snowflake backfill behaviour on view change (if enabled)
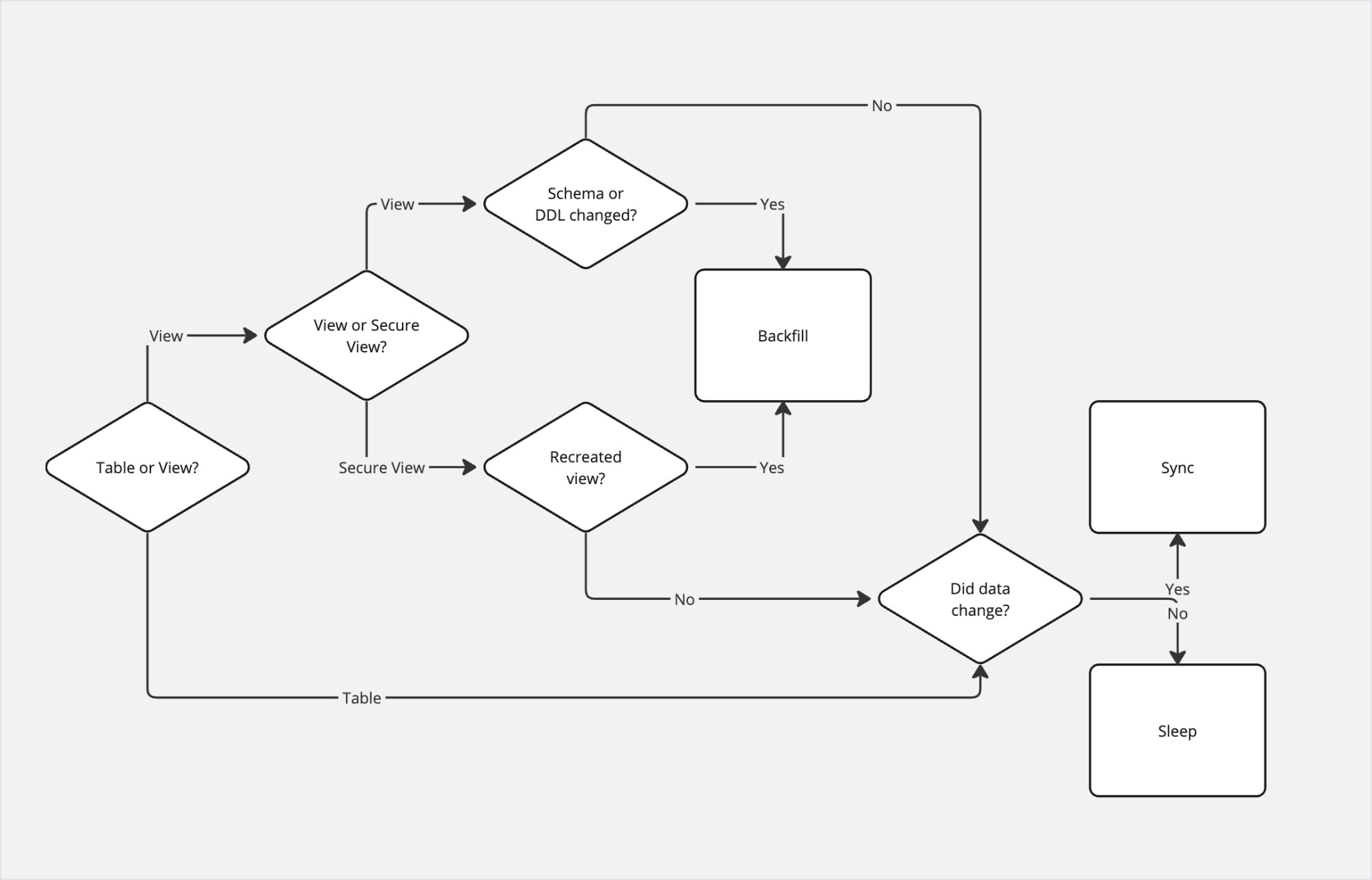
NOTE:
Bobsled detects if a Secure View has been recreated by inspecting ‘created_at’ field in ‘SHOW VIEWS’ query results.
Key Benefits
Data Consistency: Ensure destination shares always reflect source data accurately.
Automation: Bobsled detects and initiates necessary backfills to save time and effort.
Considerations
Sources with TTL policies: When backfilling from sources that maintain a TTL policy, any data in the share older than the TTL policy will not be restored.
Example: The share has been active for 30 days. The source bucket has a 10-day TTL policy. Once a backfill is initiated, this share will only have data from the most recent 10 days available in the source bucket.